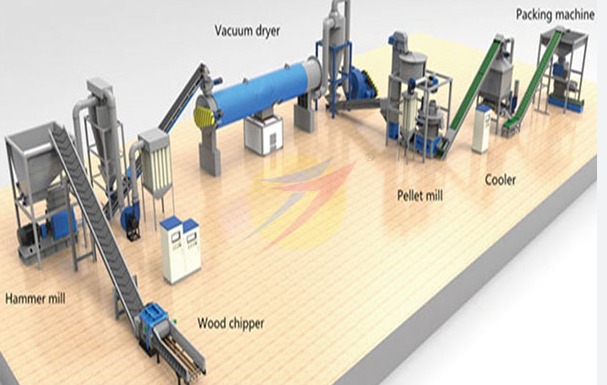
Here's a basic overview of how a biomass pellet machine works:
- Material Preparation: The first step is to prepare the biomass material. This often involves grinding or chipping the raw material into smaller pieces. The material needs to be in a consistent size and moisture level for efficient pelletization.
- Feeding: The prepared biomass material is fed into the pellet machine's hopper or feeder. Some pellet machines have a conditioning chamber where steam or water can be added to adjust the moisture content and improve pellet quality.
- Compression and Extrusion: Inside the pellet machine, the biomass material is subjected to high pressure and temperature. The combination of heat and pressure softens the material and causes it to bind together. A die with small holes is used to shape the biomass into cylindrical pellets. As the material passes through the die, it is compressed and extruded, forming the pellets.
- Cutting and Cooling: Once the pellets are formed, they are cut to the desired length by a rotating cutter or knives. The newly formed pellets are often quite hot, so they are typically cooled in a separate cooling chamber or with airflow to reduce their temperature and moisture content.
- Screening and Packaging: After cooling, the pellets may go through a screening process to remove fines and ensure uniform size. The finished pellets can then be packaged in bags or stored in bulk for distribution and use.
- Packaging: Once the pellets are cooled and sieved, they can be packaged in
bags or stored in bulk for distribution and use.
There are different types of biomass pellet machines available, including flat die pellet mills and ring die pellet mills. The choice of machine depends on factors like the scale of production, the type of biomass material, and the desired pellet quality.
Biomass pellet production has gained popularity as a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. It's used in residential heating, industrial boilers, power generation, and more, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.